Table of Contents

Basics about Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
1. what is miniature circuit breaker?
In electrical systems, safety is of utmost importance. One crucial component that ensures the safety of electrical circuits is the Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB).
MCBs are automatic switches that protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. They are essential in preventing potential fires and electrical hazards.
This article will provide an in-depth exploration of the various types of MCBs available in the market and their specific applications.
2. How does a miniature circuit breaker work?
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an electromechanical device designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overcurrents, such as those resulting from an overload or a short circuit. It operates on two principal mechanisms:
Thermal Protection (Overload): Utilizes a bimetallic strip that heats and bends with increased current flow, causing the breaker to trip and disconnect the circuit, thereby preventing overheating and potential damage.
Magnetic Protection (Short Circuit): Employs an electromagnetic solenoid whose magnetic field increases with the current flow. In the event of a short circuit, the sudden surge in current creates a strong magnetic field, triggering a plunger to trip the breaker and instantly disconnect the circuit.
3. What is the advantage of miniature circuit breaker?
Upon detecting these conditions, the MCB trips, thereby interrupting the circuit to prevent damage. The MCB can be manually reset after addressing the fault, allowing for continued protection and operation without needing replacement, unlike a fuse.
This makes MCBs a reliable, reusable, and precise solution for circuit protection in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Types of MCB

1. MCB Type B: General Purpose MCBs
MCB Type B is the most commonly used and versatile type of MCB in electrical systems. These MCBs offer protection against overcurrents resulting from both resistive and inductive loads. These MCBs, including the Wi-Fi MCBs are suitable for most household and commercial applications where the connected equipment does not have high inrush currents.
2. MCB Type C: For Motor Loads
MCB Type C is specifically designed for circuits with motor loads. Motors often experience inrush currents that are significantly higher than their rated currents when starting. MCB Type C can handle these inrush currents without tripping, providing reliable protection for motor-driven systems.
3. MCB Type D: High Inrush Currents
MCB Type D is designed to handle circuits with high inrush currents. These MCBs are typically used in applications where equipment such as welding machines, transformers, or large capacitors are present. MCB Type D offers robust protection against short circuits and overcurrents caused by high inrush currents.
4. MCB Type K: Industrial Applications
MCB Type K is specifically designed for industrial applications where there is a need to protect against high short-circuit currents. These MCBs have higher breaking capacities compared to other types, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial equipment and installations.
5. MCB Type Z: Sensitive Equipment
MCB Type Z, also known as a selective MCB, is designed for circuits with sensitive equipment. These MCBs offer precise discrimination, allowing only the faulty circuit to be disconnected while keeping other circuits operational. They are commonly used in critical applications where uninterrupted power supply is crucial.
6. MCB Type AC: Alternating Current
MCB Type AC is designed for circuits with alternating current (AC) loads. These MCBs offer protection against overcurrents caused by resistive and inductive loads in AC circuits. They are widely used in residential and commercial applications where AC-powered devices are prevalent.
7. MCB Type DC: Direct Current
MCB Type DC is specifically designed for circuits with direct current (DC) loads. These MCBs provide protection against overcurrents in DC circuits, which are commonly found in solar power systems, automotive applications, and industrial equipment. MCB Type DC ensures the safe operation of DC-powered devices.
8. MCB Type F: High Sensitivity
MCB Type F, also known as a high-sensitivity MCB, offers enhanced protection against electric shock. These MCBs have a higher tripping sensitivity compared to other types, making them suitable for applications where human safety is a top priority, such as swimming pools, medical facilities, and outdoor areas.
9. MCB Type SI: Surge Protection
MCB Type SI, also known as a surge protection MCB, is designed to protect circuits from voltage surges and transient overvoltages. These MCBs feature built-in surge protection devices that divert excess voltage to the ground, safeguarding sensitive equipment from damage. MCB Type SI is commonly used in areas prone to lightning strikes and power surges.
10. MCB Type G: Ground Fault Protection
MCB Type G, also known as a ground fault protection MCB, is designed to detect and protect against ground faults, commonly known as earth leakage. These MCBs provide an additional layer of safety by quickly disconnecting the circuit when they detect a leakage current, preventing electric shock and potential damage to equipment.
Overview: MCB Major Types
| MCB Type | Features | Applications |
| Type B | Optimal for both resistive and inductive load overcurrent protection. Predominantly used in domestic and commercial environments. | Residential, commercial spaces |
| Type C | Tailored to manage motor start-up inrush currents, preventing unwarranted tripping. | Motor-driven systems, HVAC applications |
| Type D | Engineered for environments with substantial inrush currents, ensuring robust protection. | Industrial machinery, transformers |
| Type K | Designed for elevated short-circuit current scenarios, ideal for heavy-duty industrial use. | Industrial installations |
| Type Z | Offers precise tripping, maintaining circuit integrity in the presence of sensitive devices. | Critical systems, data centers |
| Type AC | Caters to AC load overcurrents, encompassing both resistive and inductive components. | AC-powered environments |
| Type DC | Specialized for DC circuit overcurrent protection, vital for solar and automotive systems. | Solar installations, electric vehicles |
| Type F | Features enhanced sensitivity to electric shock, prioritizing human safety. | Public pools, healthcare facilities |
| Type SI | Incorporates surge protection to shield against voltage spikes and transients. | Lightning-prone areas, surge-sensitive environments |
| Type G | Detects and isolates ground faults, augmenting safety by mitigating electric shock risks. | Safety-critical applications, leak-prone areas |
Discover more Circuit Breakers with Santo
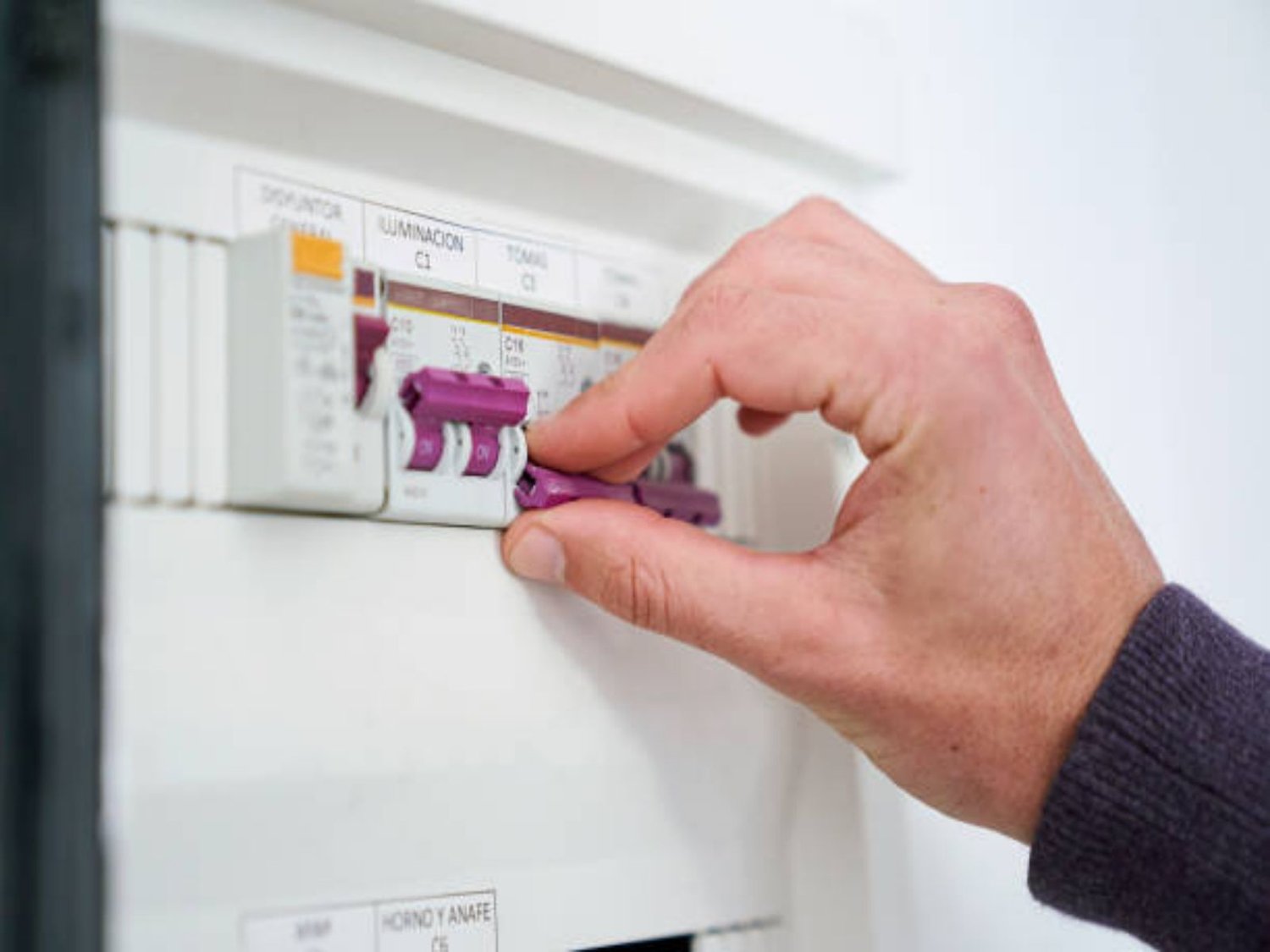
Bonus: How to Install a Miniature Circuit Breakers?
To install a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), first ensure the main power supply is off to avoid electrical shock. Mount the MCB on the distribution board's DIN rail and connect the live wire to the MCB's input and the load wire to its output, adhering to the manufacturer's guidelines for wire gauge and torque.
After installation, check all connections are secure, then restore power and test the MCB to ensure proper operation. For safety and compliance, consider hiring a certified electrician.
